
Effective handwashing techniques: between the fingers. Hand washing is very important to avoid the … [+]
GETTY
We’ve all been hearing “wash your hands” as the singular best way to stay healthy during these dark days of Covid-19. It seems so basic— it’s what we teach toddlers even before they are able to stand up on their own. Every parent has asked their child, even tweens and teens: “Did you wash your hands?” followed by a “Yes” and an eye roll, followed by “With soap?” followed by…. silence and said eye rolling cum slouching child returning to the sink to wash with said soap. Washing with soap and water is not a new phenomenon that became a new hot latest and greatest practice just weeks ago. The ancient Babylonians used soap in 2800 B.C.E.
While personal use of masks and gloves by non-healthcare workers is a relatively new source of heated debate, washing with soap and water crosses all political lines, religious differences, thoughts on climate change, and personal health disputes. We all know it’s the best. Even better than portable hand sanitizer. Better than plain water, and better than sanitizing wipes.
What is it about soap that gives it such superpowers?
Macro close up of soap bubbles
GETTY
Plain old hand soap, no, not antibacterial soap (remember, this is a virus devastating us, not a bacteria), contains molecules that are actually called “soap molecules.” They contain a hydrophobic (water-hating, or water-fearing) end and a hydrophilic (water-loving) end. When mixed with water, the components of a soap molecule line up so that the water-loving ends are facing out, and the water-hating ends are facing in.
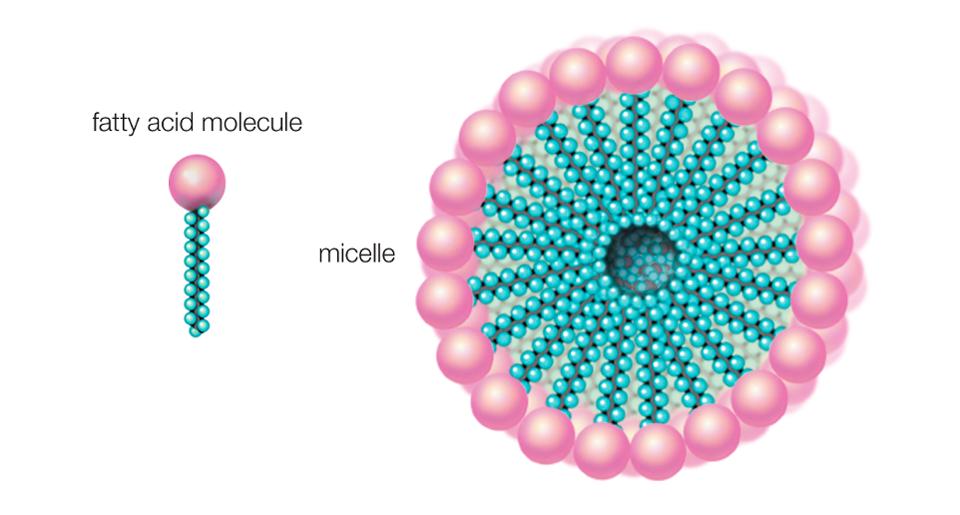
When Dissolved In Water, Fatty Acids In Soap Form Micelles, The Hydrophilic Ends Turned Outward And … [+]
UNIVERSAL IMAGES GROUP VIA GETTY IMAGES
When dissolved in water, the components in soap form circular “micelles,” exposing all of the water-loving ends outward. The coronavirus is coated with lipids and proteins, The hydrophilic (water-loving) component of soap acts to dissolve the lipids and break down the proteins, both of which actions help prevent the virus from entering the cells on the skin. Hand sanitizer containing at least 60% alcohol also has effects on this virus. The alcohol acts to disrupt RNA molecules in the virus, preventing viral replication (in other words it blocks the virus from making copies of itself). But soap is slightly superior, as there is the scrubbing part that comes with hand washing with soap and water.
The World Health Organization (W.H.O.) has provided a now highly viewed poster about hand washing technique, which emphasizes not only coating the hands with soap and water, but also includes rubbing the soap into the skin for at least 20 seconds (with the song, meme or Shakespearean monologue of your choice these days). The duration is critical, as it ensures a more thorough cleansing, as opposed to just a surface once-over one tends to do with hand sanitizers or wipes. Unlike hard surfaces such as tables, door knobs, or computer screens, skin has a more irregular, variant texture, whereby a light coating followed by a three-second rinse just won’t do the job.
Surgeons and operating room staff spend a good deal of time learning how to do a surgical scrub correctly, as well as how to don and remove hats, masks, gloves, goggles, and gowns (all now affectionately and widely known as PPE, or personal protective equipment). There’s an order and a method to this process, both before entering an operating room, before approaching the operative field (known as “scrubbing in”) as well as when leaving an operative field (”scrubbing out”), and later leaving the operating room area.
The surgical scrub prep, at first onerous and cumbersome, soon becomes second nature and so routine to anyone working in an operating room. We giggle when we watch a medical television show where the surgeon is not wearing a mask while at the scrub sink, touches his or her scrub hat after scrubbing, or (gasp!) puts on gloves before a gown. There is a precise order for donning PPE, scrubbing, and, perhaps equally as important, removing and disposing of such items. This order and technique prevent spread of infections to the person, to the patients, and to anyone in the vicinity. This is one of the reasons that health personnel literally cringe when we see people out and about with masks and gloves. Unless you work in an operating room (or another environment in healthcare settings requiring aseptic techniques), there is little information available regarding safe utilization and disposal of masks and gloves in the community. In short, these items more often provide a false sense of protection and can indeed act to spread infection. As described in a recent Forbes piece by Tara Haelle, these are doing you no service, and can actually be a disservice to you and those around you.
There is no need for everyone to get a crash course PPE donning and removal technique, nor on how to do a proper surgical scrub.
Just wash your hands. With soap. And after that, dry them. With a towel (disposable these days). Towels enable one to continue to use a bit of friction on the skin, which helps remove dirt and pathogens. Bathroom hand dryers are a big “no” these days. In 2018, a study published by the American Society of Microbiology found that these dryers literally suck up bacteria from fecal matter in the bathroom air, and spray it on each user.
To sum it up:
Wash your hands.
With soap and water.
Dry them.
With a paper towel.
Throw out the towel.
Repeat often.
Tell a friend.
Source: www.forbes.com

